Deutscher Rheumatologiekongress 2025
Deutscher Rheumatologiekongress 2025
Single-cell profiling reveals functional remodeling of CD8+ recent thymic emigrants in rheumatoid arthritis
Text
Introduction: Recent thymic emigrants (RTEs) are a distinct subset of naïve T cells that have just exited the thymus and are essential for maintaining peripheral immune balance [1]. Increasing evidence suggests that RTEs are highly responsive to inflammatory signals and may contribute to immune dysregulation [2]. However, their specific role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) remains unknown. In this study, we employed single-cell analysis to comprehensively characterize RTEs in RA.
Methods: We analyzed single-cell RNA sequencing data3 from 36 clinical PBMC samples to construct a comprehensive atlas of RTEs in human RA. Gene set enrichment analysis was performed to score RTEs across different disease states and subtypes. Differential gene expression analysis and KEGG enrichment were conducted on RTEs and surrounding T cell subsets. Additionally, we investigated cell–cell communication, developmental trajectories, and metabolic features to delineate the functional landscape of RTEs in RA.
Results: Our analysis revealed that CD8+ RTEs exhibited a more distinct RTE signature compared to CD4+ RTEs, with higher expression specificity for known markers—both in RA patients and healthy controls. Notably, in RA patients, differentially expressed genes in CD8+ RTEs were enriched in metabolism-related pathways such as the mTOR signaling pathway, fatty acid metabolism, and pentose phosphate pathway. In contrast, CD8+ RTEs in healthy controls showed enrichment in pathways like fructose and mannose metabolism. Further metabolic pathway analysis revealed that CD8+ RTEs in RA displayed higher levels of glycolysis and lipid metabolism compared to other subsets. Additionally, the synthesis of steroid hormones was found to be reduced (Figure 1 [Fig. 1]). Cell–cell communication analysis further revealed that CD8+ RTEs accounted for 75% of key interaction events in RA (Figure 2 [Fig. 2]). Among these, MHC-I-mediated signaling emerged as the predominant communication type, suggesting a pivotal role of antigen presentation and immune surveillance in the functional rewiring of CD8+ RTEs. Trajectory analysis indicated that CD8+ RTEs represent one of the earliest developmental T cell states, with activation levels positively correlated with age and CRP level.
Figure 1: KEGG Enrichment pathways in Normal and RA samples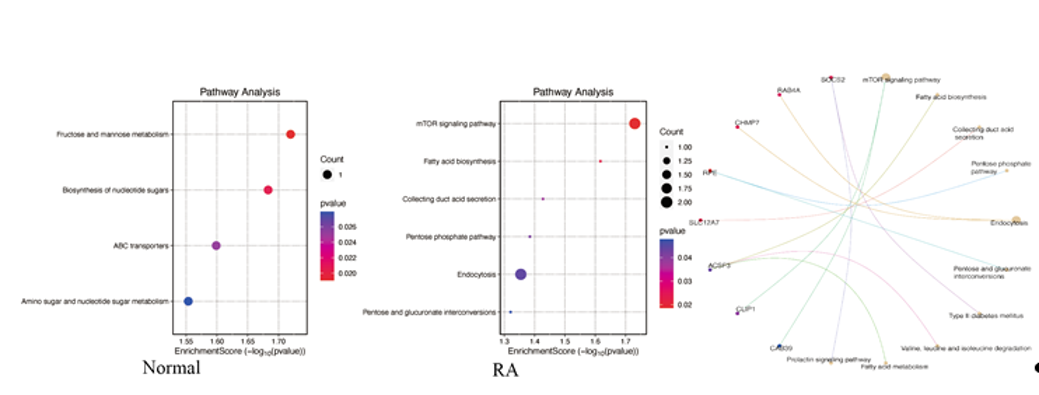
Figure 2: Cell-cell communications in Normal and RA PBMC samples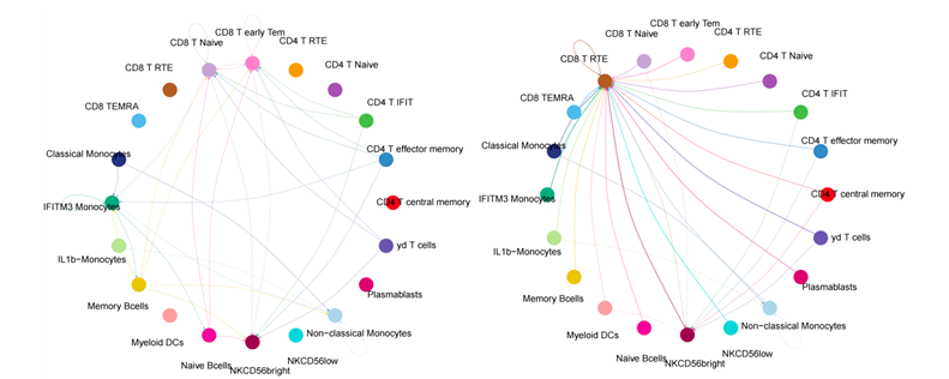
Conclusion: In rheumatoid arthritis, CD8+ RTEs represent a metabolically reprogrammed T cell subset with active participation in intercellular communication. Their functional dynamics may indicate disease progression and prognosis in RA.
References
[1] Ao YQ, Jiang JH, Gao J, Wang HK, Ding JY. Recent thymic emigrants as the bridge between thymoma and autoimmune diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2022 May;1877(3):188730. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2022.188730[2] Friesen TJ, Ji Q, Fink PJ. Recent thymic emigrants are tolerized in the absence of inflammation. J Exp Med. 2016;213(6):913-20. DOI: 10.1084/jem.20151990
[3] Binvignat M, Miao BY, Wibrand C, Yang MM, Rychkov D, Flynn E, Nititham J, Tamaki W, Khan U, Carvidi A, Krueger M, Niemi E, Sun Y, Fragiadakis GK, Sellam J, Mariotti-Ferrandiz E, Klatzmann D, Gross AJ, Ye CJ, Butte AJ, Criswell LA, Nakamura MC, Sirota M. Single-cell RNA-Seq analysis reveals cell subsets and gene signatures associated with rheumatoid arthritis disease activity. JCI Insight. 2024 Jul 2;9(16):e178499. DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.178499




