Deutscher Rheumatologiekongress 2025
Deutscher Rheumatologiekongress 2025
Routine use of Ixekizumab for the treatment of psoriatic arthritis in Austria – data from the national BioReg Registry
Text
Introduction: Ixekizumab, a high-affinity humanized antibody selectively targeting IL-17A, has demonstrated its efficacy and safety in treating patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) in randomized controlled trials [1], [2], [3]. Observational studies and registries provide important real-life data complementing the information obtained from clinical trials [4]. This study presents data on PsA patients treated with ixekizumab in routine clinical care in Austria.
Methods: Adult PsA patients from the Austrian BioReg registry who initiated treatment with ixekizumab between 2018 and 2023 were included in this study. The primary objective was to determine the treatment retention rate at week 52 and to assess treatment persistence using the Kaplan-Meier method. Further analyses involved descriptions of the reasons for treatment discontinuation, patient profile and treatment patterns. Effectiveness at week 26 and 52 was assessed using tender joint count (TJC) and swollen joint count (SJC). Categorical variables are presented as numbers (%), and continuous variables as mean ± standard deviation (SD).
Results: A total of 73 patients were included (56.0% female, mean age: 56.0±12.7 years, TJC: 4.8±5.6, SJC: 2.0±2.9), more detailed baseline characteristics are listed in Table 1 [Tab. 1]. Eighty-five percent of the patients were treated with at least one biologic or targeted synthetic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug (b/tsDMARD) prior to ixekizumab. At week 52, 41 of 73 patients were still being treated with ixekizumab, corresponding to a treatment retention rate of 63.8% (95%CI: 53.5–76.0%). One-year treatment persistence is shown in Figure 1 [Fig. 1], the median time to discontinuation was 139.14 weeks. Ineffectiveness was the most prevalent reason for treatment discontinuation (62%), followed by intolerance (31%). At week 26, patients had a mean TJC of 2.49±4.88 (n=41) and a mean SJC of 0.43±0.86 (n=42). At week 52, the corresponding values were 1.72±3.52 and 0.34±0.94 (both n=32), respectively.
Table 1: Baseline characteristics of patients treated with ixekizumab as recorded in the Austrian BioReg registry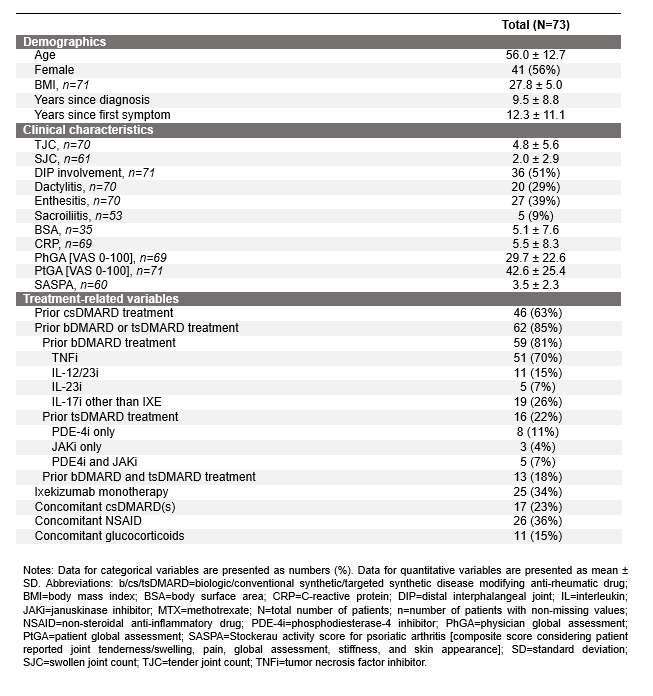
Figure 1: Persistence of patients treated with ixekizumab as recorded in the Austrian BioReg registry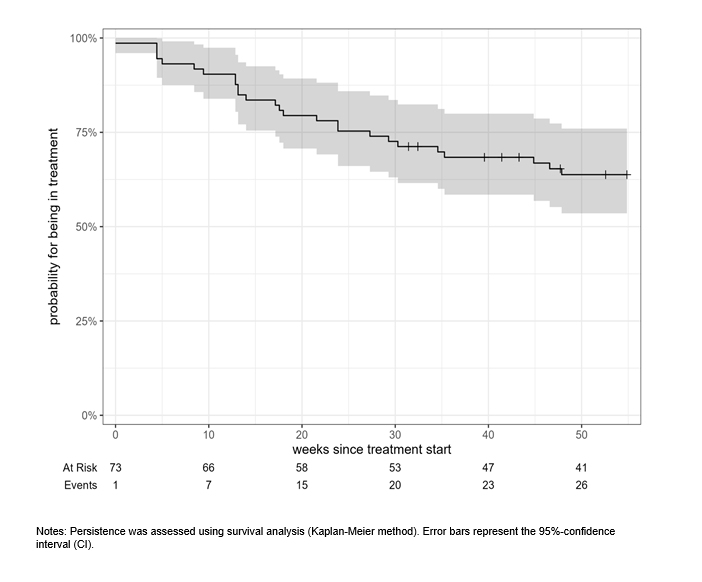
Conclusion: This observational registry study provides real-world data on PsA patients treated with ixekizumab in Austria. The high 1-year retention rate and low joint-specific scores at follow-up visits support the effectiveness of ixekizumab in routine clinical care even after failure of prior b- or tsDMARD treatment.
Disclosures: AB received fees from BioReg for data analysis. VB and TR are Lilly employees. BR received consultation and/or speaker honoraria from Eli Lilly. PS received consultation and/or speaker honoraria from Eli Lilly. JH received consultation and/or speaker honoraria from Eli Lilly. RFS has no conflicts of interest to disclose regarding this project. The authors would like to acknowledge Dr. Manuel Zoidl for writing contributions. Eli Lilly funded the study and the medical writing support.
Literatur
[1] Mease PJ, van der Heijde D, Ritchlin CT, Okada M, Cuchacovich RS, Shuler CL, Lin CY, Braun DK, Lee CH, Gladman DD; SPIRIT-P1 Study Group. Ixekizumab, an interleukin-17A specific monoclonal antibody, for the treatment of biologic-naive patients with active psoriatic arthritis: results from the 24-week randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled and active (adalimumab)-controlled period of the phase III trial SPIRIT-P1. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017 Jan;76(1):79-87. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209709[2] Nash P, Kirkham B, Okada M, Rahman P, Combe B, Burmester GR, Adams DH, Kerr L, Lee C, Shuler CL, Genovese M; SPIRIT-P2 Study Group. Ixekizumab for the treatment of patients with active psoriatic arthritis and an inadequate response to tumour necrosis factor inhibitors: results from the 24-week randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled period of the SPIRIT-P2 phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2017 Jun 10;389(10086):2317-27. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)31429-0
[3] Mease PJ, Smolen JS, Behrens F, Nash P, Liu Leage S, Li L, Tahir H, Gooderham M, Krishnan E, Liu-Seifert H, Emery P, Pillai SG, Helliwell PS; SPIRIT H2H study group. A head-to-head comparison of the efficacy and safety of ixekizumab and adalimumab in biological-naïve patients with active psoriatic arthritis: 24-week results of a randomised, open-label, blinded-assessor trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020 Jan;79(1):123-31. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-215386
[4] Maissenhälter BE, Woolmore AL, Schlag PM. Real-World-Evidence-Forschung auf Basis von Big Data. Onkologe. 2018;24:378–89. DOI: 10.1007/s00761-018-0354-7




