German Congress of Orthopaedics and Traumatology (DKOU 2025)
Deutscher Kongress für Orthopädie und Unfallchirurgie 2025 (DKOU 2025)
Midshaft clavicle fractures with associated ipsilateral acromioclavicular joint injuries: Current concept review
Text
Objectives and questions: Isolated midshaft clavicle fractures (MCF) and acromioclavicular joint (ACJ) injuries are common, but simultaneous cases are rare and often receive insufficient clinical attention, resulting in missed diagnoses. Moreover, there is no consensus on the injury mechanism, classification, and treatment, and the prognosis remains poorly summarized. This review aims to provide an overview of MCFs with ipsilateral ACJ injuries, focusing on injury mechanism, classification, treatment, and prognosis.
Material and methods: We searched the literature published between 1962 and 2024 on PubMed, Web of Science, and EMBASE using the search terms “clavicle fracture [Title/Abstract]) AND (acromioclavicular [Title/Abstract])”. Studies reporting clinical outcomes in patients with MCF and ipsilateral ACJ injuries were included. 37 studies were included after screening. The study quality was assessed using the Joanna Briggs Institute Critical Appraisal Checklist. Data on study design, patient demographics, treatment approaches, and outcomes were extracted for qualitative analysis. We then summarized key findings and presented our insights.
Results: MCFs with ipsilateral ACJ injuries are often associated with comorbidities such as rib fractures, hemopneumothorax, scapula fractures, neurovascular injuries, and atypical MCF displacement patterns. These cases should raise suspicion for combined injuries. Due to the “floating” nature of the lateral clavicle, the “Piano Key Sign” is typically negative and not reliable for diagnosis. Initial ACJ evaluation may be inconclusive, so reevaluation after MCF fixation is recommended. Type IV ACJ injuries can be underestimated on anteroposterior radiographs, and additional axillary radiographs and CT scans may better visualize posterior clavicle displacement. Most researchers believe ACJ capsule and ligament damage occurs first, but is insufficient to cause significant dislocation, suggesting that isolated MCF may involve combined ACJ injury with intact coracoclavicular ligaments. Notably, most patients reported favorable outcomes without major complications within two years, regardless of treatment approach.
Discussion and conclusions: MCFs with ipsilateral ACJ injuries are rare and often missed when ACJ injuries are mild. The injury mechanism is unclear, and no classification system exists to indicate severity. These injuries are typically treated separately without a unified protocol. Despite promising outcomes, further studies are needed to address these issues and improve understanding of long-term results.
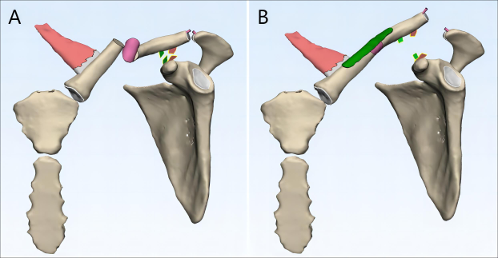
Figure 1 [Abb. 1]
Figure 1: Graphic illustration of the reason for underestimating acromioclavicular joint injuries with ipsilateral clavicle fractures. (A) Combined clavicle fracture and ligament rupture can cause downward displacement of the lateral clavicle, masking acromioclavicular joint dislocation on imaging; (B) The injury becomes apparent post-clavicle fixation, revealing a “delayed” dislocation.